How to Create Marketing Drawings Architecture Plans Representation
What Is a Structure Plan? Definition, Uses, and History
Structure plans differ from maps, which comprehend much larger areas and have much larger scale ratios. Rather, a typical construction plan depicts only one structure and its parts or sections. By changing perspectives and details, it tin exercise so in a number of ways.
Construction drawings also fill an of import role in the overall construction planning procedure. Building departments and local governments must review plans before they will upshot construction or renovation permits. Planners judge building cloth and labor costs based on plans. In the pre-construction planning and scheduling phase, contractors use plans to create piece of work breakdowns and schedule construction tasks. In one case construction gets underway, drawings guide the work.
As physicist John Swain writes for the Boston Globe, blueprints originated after an 1861 discovery by French chemist Alphonse Louis Poitevin. He constitute that the chemical ferro-gallate, derived from gum, could permanently turn a brilliant shade of blue when exposed to strong light. To create a pattern, one would first place the translucent paper of an architectural drawing over paper coated with unexposed ferro-gallate. Then, they would expose the paper layering to stiff natural light. As low-cal passed through the translucent top sheet, turning the ferro-gallate canvass below it blue (except for where the drawn lines on the top sheet prevented light from passing through to the bottom sheet), the chemic combination would reproduce a complex, finely detailed drawing in minutes.
This procedure was called contact printing, and the result was a blueprint: a white-lined, blue sheet of paper that formed a drawing. Blueprints toll a fraction of the money and time that other gimmicky reproduction techniques did, so they quickly gained popularity among non only architects, simply also scientists and artists who wanted to quickly reproduce complex diagrams.
True blueprints roughshod out of use in the 1950s. The proper name stuck, however, and today we continue to call complex pattern drawings blueprints. Of form, since the mid 20th century, architectural drawings have undergone several evolutions. With CAD (reckoner-aided pattern) software, we can now hands visualize them in 3D with varying levels of detail and from a variety of perspectives.
CAD software simplifies the builder'south work considerably. Blueprints' background colour fabricated them very difficult to write on, and information technology's much easier to brand pattern changes digitally rather than on newspaper.
Though modern structure plans vary greatly in scale and complexity, representing everything from small-scale residential to large commercial projects, all construction plans contain the same essential elements. All buildings, no matter how complex, consist of structural components, mechanical systems, and finishes.
A construction programme volition provide the same kind of data regardless of the size or complexity of a project. For example, a floor plan will provide a bird's eye view of room dimensions and installations regardless of whether it'south drawn for an apartment or a convenience store, and a mechanical plan might detail mechanical systems for either a kitchen or a laboratory. If you tin can read ane, you tin read the other; merely the level of complication will vary.
Construction plans are unlike from a construction company'southward business plans, which tell footling about specific construction projects and more well-nigh how a visitor wants to develop its business. Construction plans also differ from specifications: A construction plan tells you what you volition build, while specifications tell you lot how you build it.
Specifications will include information on materials yous utilise, installation techniques, and quality standards. While most designers and architects will follow these methods for presenting data, others will annotate specs on structure plans, and so the difference isn't always articulate cut. If the information in the specifications conflicts with that of the plans, the usual do is to follow the specs over the plan.
General contractors, subcontractors, and tradesmen must have a deep knowledge of plan reading, and owners of large commercial projects will want to empathise at least the broad strokes of a program. Small project owners accept an advantage if they are familiar with construction plans because they tin sympathize exactly what the builders are going to be build. If you're a homeowner and you don't empathize the builder or designer depicts the project, enquire them then you're on the same folio before construction gets underway.
In fact, the professionals at HomeBuildingSmart recommend that you familiarize yourself with house plans before showtime a construction project, so you know what your tastes are and can provide useful input as the architect creates your construction plan. Recollect, you tin alter plans, but y'all can't undo construction. Then, iron out the details while they're still only on paper.
Blueprints tin can seem arcane when yous're starting out, only with exercise, reading them volition go easier. And then, if yous're a project owner, don't shy abroad from construction plans: Make sure you understand what'south going on with your project.
Transform structure management with Smartsheet. See for yourself.
Smartsheet enables y'all to runway each projection with its own dedicated project sheet and get a unified view across all projects in a dashboard. Monitor tasks across projects and capture on-site bug through a unproblematic form on desktop or mobile.
Watch a free demo
Construction Plans: A Foundation Document in the Construction Process
Home owners who want to build new houses by and large start with rough ideas of their desired home structures and layouts. They may select an architect or designer to typhoon the business firm for them. (The National Council of Building Designer Certification program offers communication on how to evaluate designers for residential projects.) Ideally, homeowners provide input as the architect draws up a ready of plans until they accomplish a solution that satisfies everyone.
In one case the plans are gear up, the homeowner will seek a contractor to build the firm. Some contractors don't actually perform construction work themselves, simply rather consul it to subcontractors and tradesmen (though this is unusual for smaller projects). The builders will need a variety of construction plans to bring the architect's ideas to life.
Regardless of the size of the project, construction nearly always gain systematically. The get-go stage, planning, is generally a conversation among projection owners and stakeholders who determine what objectives the project should reach, whether they are doable, and how and when they will be met.
During the pattern stage, the projection owner or client works with the architect to come up with a finalized building pattern that is buildable and meets the client'due south requirements. The level of collaboration hither varies from projection to project.
This stage is followed past pre-structure, when planners, contractors, and inspectors examine the design for constructability and value - therefore, this phase may upshot in changes to the plans. Contractors as well bid for the project during this phase. Once yous sign with a contractor, the builders procure materials, resources, labor, and expertise for the projection.
Construction is usually the longest phase of whatever building project. General contractors, subcontractors, and tradesmen work to bring the builder'due south plans to life. When construction is consummate, the building goes through commissioning, which is the process of making sure that everything works as it should before people occupy the building.
You define many construction projection types by cease use, but projects are broadly classified as either residential or commercial. Residential refers to relatively small projects that builders complete for homeowners, and commercial acts as an umbrella term for annihilation from warehouses to hospitals.
However, builders may categorize projects even more narrowly, and some architects, engineers, and contractors specialize in detail niche areas, such as commercial (office buildings), instruction (schools), healthcare (hospitals), civil (highways and bridges), retail (stores), or industrial (factories, distribution centers) structures.
No ii projects are exactly the same, fifty-fifty though there is a large degree of repeatability - the replication of a proven construction model - in some projects.
Because every project is unique, planning needs to be specific and tailored to the circumstances. Designers customize residential projects, for instance, to come across a variety of private needs, such as the number of rooms, bathrooms, garage bays, and stories. The project planner must take into account the infinite available and decide how to make the house'south exterior fit the possessor's taste and the neighborhood. The designer must also make the internal layout fit the structural elements, architectural style, and intended usage patterns.
For home sites that don't pose special challenges, such every bit gradient or space restrictions, owners may want to save money by using stock plans. Rather than designing a custom plan for a specific owner and site, architects pattern stock plans for flexibility and to appeal to a wide variety of tastes. Stock programme companies sell the same basic programme over and over - they sometimes include slight modifications to fit an possessor's needs, but the degree of individualization is very limited.
Stages in Designing and Drafting Construction Plans
Architects iterate custom plans several times during the design process. The American Institute of Architects divides the design process for any construction project into five phases, and includes plan revision in the start three phases, and sometimes the 4th besides.
The first stage, schematic blueprint, involves creating multiple preliminary designs based on the project owner's requests and the site. Usually, the designer prepares 2 or three of these preliminary designs, and the possessor picks the one they like best equally a starting indicate for modification. A rough cost gauge is also fastened to each design.
The design evolution phase is a dorsum-and-along give-and-take between the architect and projection owner every bit they effort to reach a consensus over the project design. This phase is followed by the structure documents phase, when the architect uses the agreed-upon blueprint to create a set of precise construction plans and detailed specifications. The contractor will use these for bidding and to apply for structure permits.
Project stakeholders may consider the building'due south design and structure documents finalized by the terminate of the 3rd stage, simply it'due south non unusual for contractors to suggest design amendments during the fourth phase, bidding. This stage can be function of a process chosen value engineering, the attempt to increase the value-to-cost ratio of a structure. Value engineering seldom results in major changes, just in some cases, it may necessitate updating or resubmitting the permit application. The final phase, construction assistants, involves the architect'south oversight of the construction process to brand sure everything is going co-ordinate to plan.
The project's rules, as stated in the specifications, contract, weather condition, and special conditions, govern the construction process. The specifications encompass materials, installation techniques, and quality standards. The contract and all conditions are collectively referred to as the project contract. They delineate the roles and responsibilities of both the projection possessor or client and the contractor.
The specifications and project contract course the basis of the contractor-client relationship. Therefore, it'due south not surprising that the highest numbers of construction disputes worldwide are directly related to contractual issues.
According to blueprint and consultancy house Arcadis' Global Construction Disputes Report for 2016, the leading cause for contract disputes was a failure to properly administrate the contract, followed by poorly drafted or incomplete and unsubstantiated claims, errors, or omissions in the contract,
incomplete pattern information or employers requirements, or the parties' failure to understand or comply with the contract.
In Due north America, the average time to dispute resolution was about 13.5 months in 2015 - this illustrates the demand for clarity and thoroughness in construction plans, specifications, and contracts if a building project is to go along smoothly.
How Construction Plans Fit into Construction Planning
Construction plans are part of the structure planning process, which is ane stage of the structure project direction lifecycle. Before we become into more detail on structure plans, however, let's recap the chief principles of construction project management.
Construction planning involves defining all the steps involved in building a construction, splitting and arranging these into a logically ordered serial of performable tasks, and so deciding what'southward necessary (people, equipment, and materials) to complete each task successfully.
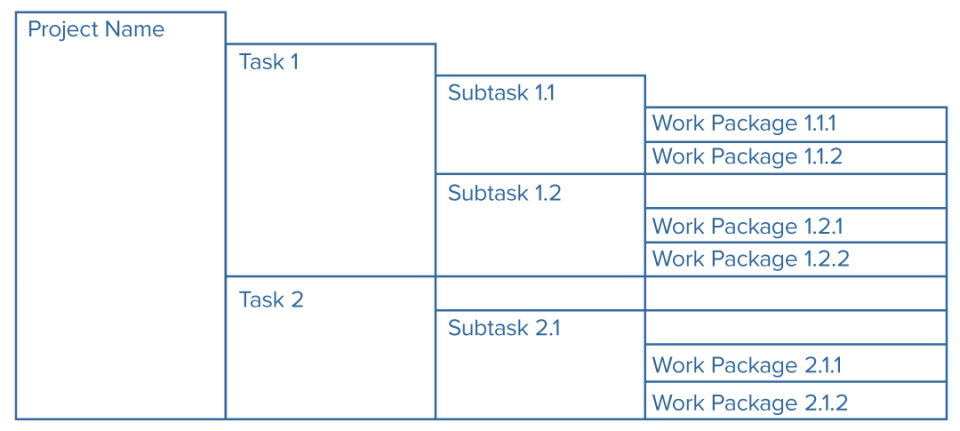
A construction plan is a prerequisite here, since you'll demand to know what you're building before y'all tin ascertain all the necessary steps. A work breakdown construction, a diagram that depicts all deliverables, represents the project piece of work in a bureaucracy of work packages that each comprise a serial of tasks. Laying bath tiles is an example of a projection deliverable: It would comprise tasks like applying cement, placing tiles, and grouting.
The consummate piece of work breakup structure is the footing of the project schedule, which tells y'all when each job should start and end in order for the building to be ready on time. To arrive at the schedule, structure planners determine task durations and establish the precedence relationships between tasks.
Task durations are the lengths of time required to complete each chore, and are determined by a number of factors. Some of these factors are controllable (for case, the number of personnel or the type and availability of equipment needed to complete a chore) and some are uncontrollable (the fact that cement must dry out for several hours before the next process can happen, regardless of the resources bachelor). Experienced builders approximate job durations based on how long it took them to exercise similar tasks in prior projects. Often, planners will use statistical techniques, such as program evaluation and review technique (PERT) to judge the fourth dimension required to complete a chore.
Precedence relationships are the logical order in which y'all will complete tasks. A combination of bones task logic — figuring out what must happen earlier, during, and after performing a specific job — and concrete or practical constraints determine precedence relationships. Builders take an intuitive understanding of task logic: You accept to lay the bricks before you can paint the walls.
Other constraints that can be hard to run across in advance may affect job execution. For case, it may appear that the cabinetry squad and the painting team can work simultaneously, except that the space is besides small for all the workers.
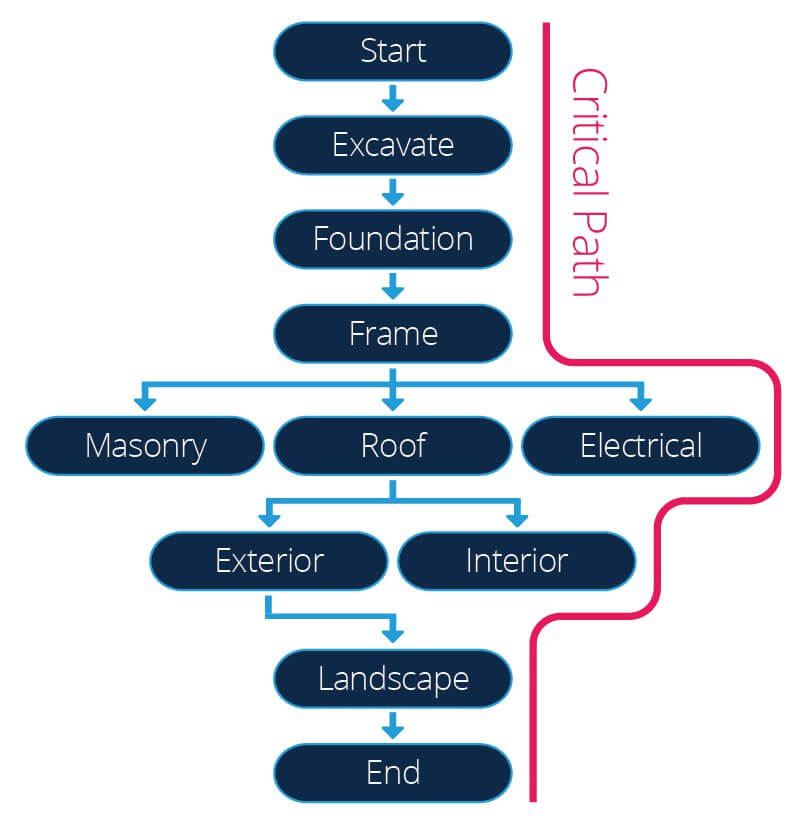
One time yous make up one's mind job durations and precedence relationships, you tin create a precedence network. A precedence network is a visual representation of all project tasks that you adapt in logical guild. Nodes, or hollow circles, represent activities that contain written job durations, and arrows between nodes stand for the order in which you perform tasks.
The precedence network drives scheduling with a technique called the critical path method (CPM). The CPM establishes the early and late showtime and end dates for tasks — that is, when you can (or must) start and stop them in gild to complete the project on time. It also identifies the projection's critical path, a sequence of activities for which any filibuster will button back the project's completion date.
Since all of these activities follow from the work breakdown structure, yous can clearly come across the importance of structure plans to the planning and scheduling of a building project.
Construction Drawings Help Planners Make Key Building Decisions
Blueprints besides shape other of import decisions, such as the pick of technology and construction methods for a project. Builders assess the calibration not only of the project every bit a whole, but also of specific components of the project, such as building materials and their position inside the construction. This procedure allows contractors and construction planners to effigy out what kind of equipment and construction techniques they'll use.
For case, a construction planner might ask whether a project requires a cement mixer truck or simply a bike-based cement mixer. And, once the crew mixes the cement, do they need to pump the mixture to the higher levels of the structure, or can they transfer information technology by pulley or even manually?
Blueprints also make it piece of cake to check if the structure conforms with building rules and codes and if it'due south ready for building departments to issue permits for new and renovated structures. Nearly jurisdictions accept building departments or councils that must issue permits for new construction or renovation projects earlier the construction work can begin.
For example, inspectors will cheque whether buildings take adequate fire protection and safely positioned windows, include enough parking, and many other details. Projection owners seeking a edifice permit communicate these details by submitting the blueprints for review. Regime let departments will pore over the plans and check for compliance with building rules and codes before giving structure the permission to pause ground.
Plan Specifications and the Structure Estimating Process
Before, we touched on specifications and how they're different from construction plans. Builders utilize a standardized coding system, such as MasterFormat, to simplify specifications and arrive like shooting fish in a barrel for all participants to communicate requirements. MasterFormat, adult past the U.S. Construction Specifications Institute (CSI) and Structure Specifications of Canada, comprises 50 major divisions of construction information for commercial and institutional projects.
In this coding system, you identify each piece of work product with a series of numbers that describes the major category and subcategory, and the type of piece of work involved. For case, masonry is in partitioning 04, and the clay unit masonry is in subgroup 21. Brick masonry gets MasterFormat number 04 21 13, which y'all would utilize on the construction program.
Construction plans help builders estimate costs, especially during the early stages of a projection when contractors are preparing bids. To arrive at a cost guess, you use a technique called quantity takeoff and prepare a document called the bill of quantities.
The quantity takeoff calculates the materials you lot demand in a structure project. Its name derives from the expression "taking off," and it lists textile quantities from the construction drawings and specifications. You listing, for example, how much forest yous require for an action, and and so y'all multiply that amount by how many times that action occurs during construction.
The quantity takeoff is a adequately specialized functioning performed by an estimator who can both read blueprints and quantify all costs for piece of work tasks without overlooking annihilation or double counting. Pinpointing costs is tricky - even for someone who can read blueprints - because architects vary in how clearly they enumerate all dimensions on structure plans. A cost estimator or quantity surveyor typically performs the quantity takeoff.
Use this quantity takeoff worksheet to get a sense of the process.
Download Quantity Takeoff Worksheet for Construction
Excel | Word | PDF
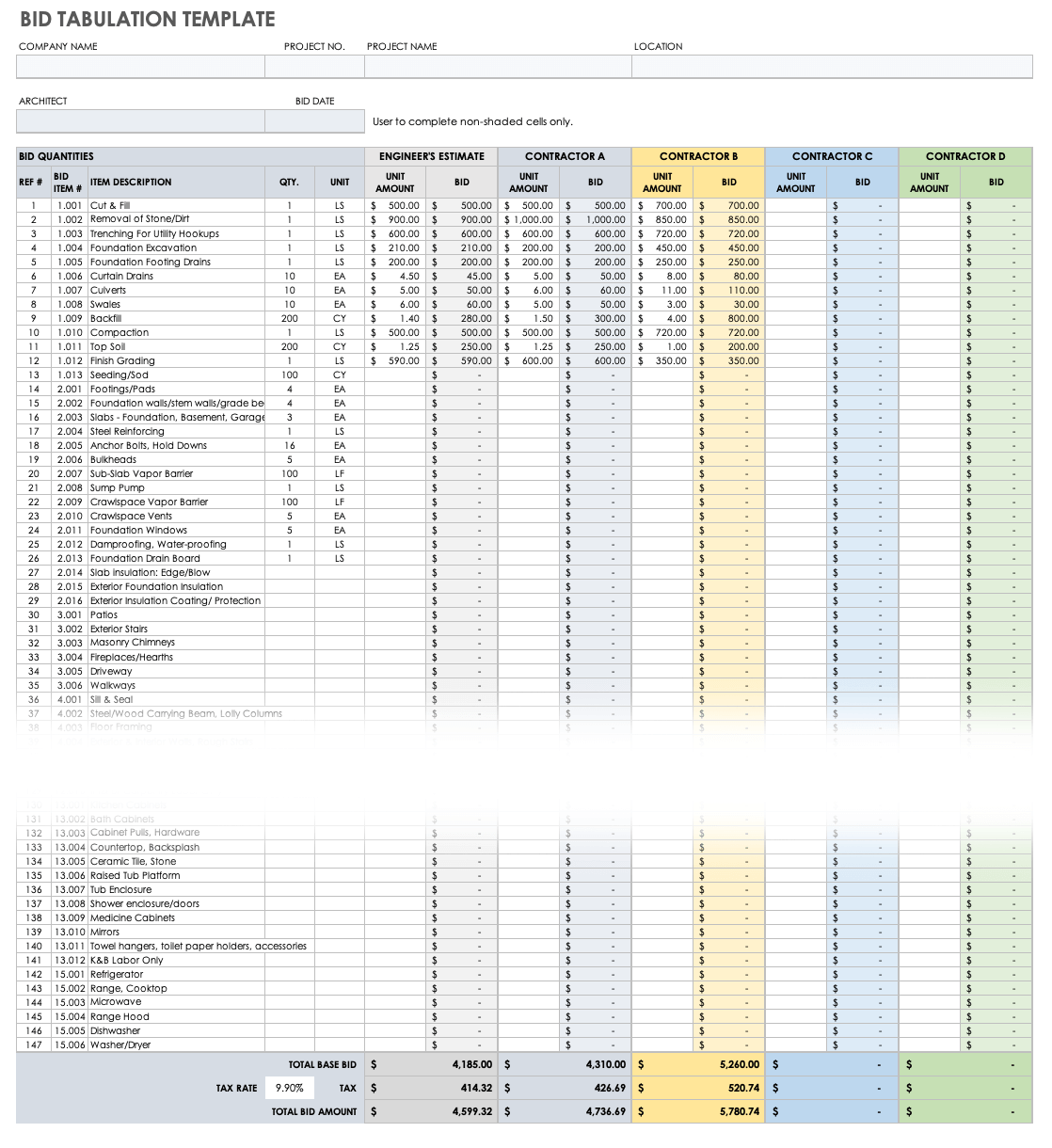
The bill of quantities lists the material quantities from the quantity takeoff, and contractors use this to make up one's mind their expenses on materials and labor for the projection. This calculation enables them to bid accurately. The bill looks like an extensive table of itemized costs: The scope of each item is described in some particular and accompanied by the number of units of each item (in terms of expanse, length, volume, or other dimensions as appropriate), the cost per unit, and the resulting full cost of that item. The nib of quantities also includes then-called contingency costs for unforeseen expenditures and waste costs and materials prone to breakage or wastage. Since the bill of quantities is an exhaustive document, yous only prepare it once you take a completed and finalized fix of construction plans.
Download Bid Tabulation Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Download Construction Computer Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Working with Construction Plans
Paper construction plans are large (about 24 by 36 inches) and consist of several pages. To beginning working with these documents, y'all'll kickoff demand to articulate a workspace where y'all tin can fully unfold the plans. Also, remember that paper plans tear and fade easily, and they deteriorate if they get wet. They're very expensive to produce and cost hundreds of dollars to replace, so make sure you're using them and storing them carefully.
You lot can easily feel overwhelmed by the sheer size and amount of detail on the plans, so the starting time step in working with them is to relax. Unlike books, plans practise non accept a unmarried starting place. Focus your attention on one corner, and and then work your way across. Good plans evidence a lot of detail and are highly accurate.
Next, figure out what kind of plan y'all're looking at: Is the perspective bird's center or side on? Is this a full view or a department? If it'south a section, which area does it pertain to?
Adjacent, check the scale. The calibration is the ratio between a construction component's dimensions on the drawing and its actual dimensions. Architects use scales with fractions, such as i/8 inch equals 1 human foot, while engineers use whole-integer scales, such as ane inch equals 100 feet. You apply architectural scales in plans for buildings, and applied science scales in plans for other construction projects, such as roads or dams. This guide from the U.Southward. Fire Administration is a skillful primer on how to select the correct scale and accurately interpret the dimensions.
If the architect possesses written dimensions for the program, use those instead of measuring the dimensions with a ruler. According to a U.S. Navy blueprint reading and sketching class, paper volition stretch or shrink over fourth dimension, which can make dimensions bigger or smaller than you intended.
You might also run across amended plans with written dimensions that don't represent to those suggested by the scale. Sometimes, in the revision process, you lot miss details. Cantankerous reference the dimensions you lot computed using a ruler and blueprint scales with those you lot've detailed explicitly on the drawing to see whether they agree. Also, try comparing different plans with elevations to see whether the dimensions add up. If you are measuring dimensions using the ruler and scale, remember to check whether someone reduced the drawings themselves during reproduction.
Since scaled dimensions aren't always authentic, an architect, engineer, or contractor should never rely on construction program scales to summate dimensions. Instead, use the dimensions written explicitly on the plans - if these are unavailable, contact the architect to obtain missing dimensions.
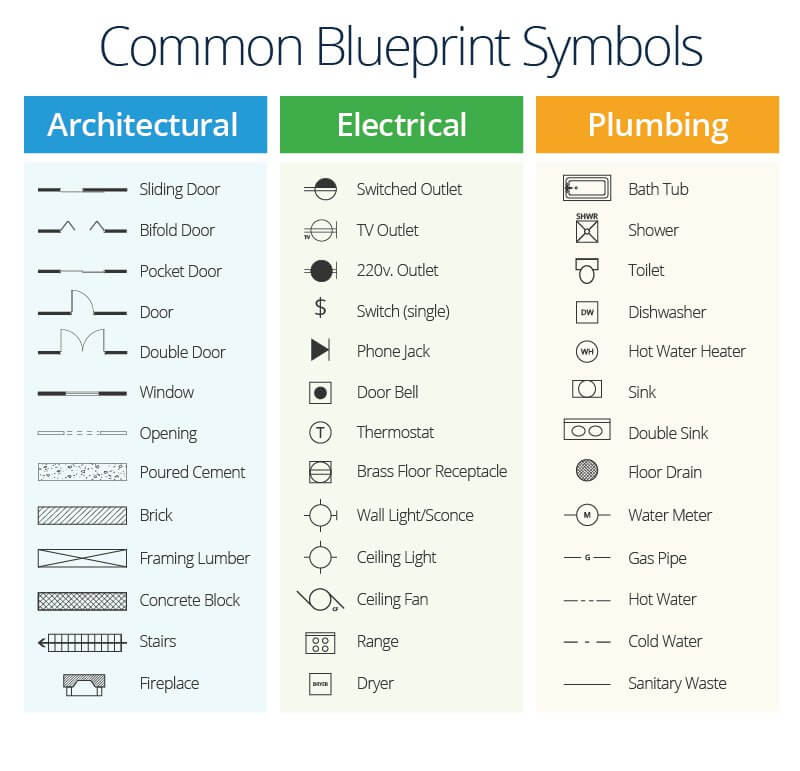
Structure plans feature symbols that represent components of the completed structure. For complex projects, architects may use hundreds of abbreviations and symbols. These represent all the structural components, down to nine different symbols for ix different types of doors. The symbols are mostly standardized, but architects have latitude to utilise their own symbols. Either way, the programme volition feature a central explaining what the symbols mean. In addition, the architect will depict elements, like stonework, using simple graphics. If you desire to brush up on blueprint symbols before you lot get your easily on a set up of plans, bank check out these gratuitous resource that HousePlanHelper.com offers.
On your plan, you lot'll notice several different types of lines. These lines bespeak everything from the visible and invisible sides of objects to the dimensions and center axes of objects. Effigy ane-iii in this Army Carpentry Field Manual details all the types of lines y'all'll meet in architectural drawings equally well equally what they mean.
The General Order of Drawings in a Fix of Structure Plans
A set of plans for a single residential project can include dozens of divide drawings (in some cases, at that place might exist more than 100). At that place's no standard practice for how many drawings a set of plans volition include: Information technology depends on the project, the builder'southward preferred level of detail, and the customs of the architect'south office. Quickly scan the entire prepare of plans before yous start, so you know what the architect has included.
The topmost canvass is the cover sheet. It includes the date, the name and location of the project, and the builder'southward proper name, accost, and contact information. The encompass sail may likewise feature an architect's rendering of the completed structure.
In many states, applying for a structure permit requires an builder or engineer to stamp the drawings. Stamped plans bear the seal of a registered and licensed engineer or architect. The professional person applies the seal with an ink postage that shows the person's name, state, license number, credential, and expiration engagement for their license.
After the cover sheet comes a program index, which lists all the drawings contained in the ready. Information technology also contains a list of commonly used abbreviations, a scale bar that indicates the programme scale, and blueprint notes if needed.
Typically, the architect will identify each drawing with a letter and number. The letter denotes the plan series: A for architectural plans, Southward for structural engineering plans, E for electrical plans, M for mechanical plans, and P for plumbing plans. The number refers to a specific program type. (For instance, A2 plans are site plans, A3 plans are flooring plans, and A5 plans are roof plans.) If the construction has multiple levels, the designer will add together boosted numbers. Each architectural firm uses their own plan-numbering conventions.
The typical order of drawings after the cover sheet and plan index is every bit follows:
- G for General Sheets: Cover sheet, plan index, and location plans
- A for Site and Architectural Plans: Floor plans, ceiling plans, roof plans, elevations, sections, wall sections, and others, depending on the builder's chosen level of item
- S for Structural Engineering: Framing plans for foundations, floors, and roofs
- Eastward, M, and P for Electrical, Mechanical, and Plumbing Components (though small residential plans may not feature these)
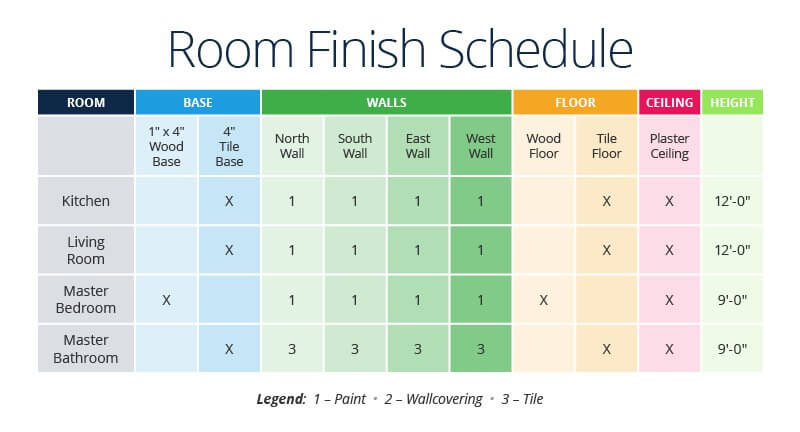
- Finish Schedule and the Door and Window Schedule: Door, window, and other interior types and finishes
- Specifications: Detailed descriptions of the materials (though these may also be appended to the A-serial architectural plans)
The level of detail (LOD) is proportional to the number of plans in the ready and determined by the builder on a project-by-project basis. The builder is responsible for making sure the construction'due south occupants and users are safety, so they mostly choose to include more item rather than less. At that place'southward also a growing tendency for architects to include more details to make information technology easier for contractors during bidding and construction. If the builder repeats a particular or dimension on multiple floors, they may annotation that it is "typical at all floors" instead of detailing it on each cartoon. Information technology is the contractor's responsibility to make certain they include these repeated details in their estimates.
Each drawing will also feature a title cake in the lower-correct corner, which lists the proper name of the specific drawing, the drawing number, the proper name of the party who prepared the cartoon, the engagement, the record of approving, and the scale. Architects may create their drawings on gridded sheets to brand pinpointing the location of various construction components easier if people are viewing the sheets simultaneously from remote locations.
If you've revised a drawing, you'll also include a revision block (usually in the superlative-correct corner of the drawing simply sometimes every bit role of the title block). Bank check the revision block to make sure you're looking at the latest approved drawing. A numbered bubble indicates a revision on a cartoon. In a corner of the drawing, you lot provide a record of revision dates and descriptions with corresponding numbers, ordinarily in easily recognizable shapes, such as a triangle or octagon. If yous make revisions, a good practice is to insert the new canvas in front of the canvas you're changing. You tin fold the erstwhile sail in on itself and tape information technology closed. Mark the sheet number "void."
You'll also hear references to two other types of drawings: redline drawings and as-built drawings. Redline drawings, so named because y'all draw them in red over the original construction plans, indicate where the actual constructed construction differs from the original program and typically indicate just minor changes. As-congenital drawings incorporate the changes from redline drawings, in upshot making them official and depicting the concluding structure as built.
No prepare of drawings is ever perfect, and there volition be discrepancies betwixt different plans that feature the aforementioned structural components. To shift responsibility for these discrepancies onto the builder, the architect will typically specify that the contractor follow the highest standard of quantity or quality in instance of alien data.
Additional Plans for Steel Construction
The construction plans for a steel structure will typically feature other drawings in addition to the full general plans, which depict the main members of the steel structure, detail their size and material, and evidence their position relative to each other.
Fabrication drawings detail the size, shape, and material for each member of the structure every bit well as the ways in which each member connects or attaches to other members. You use the fabrication drawings to procure the required materials for construction.
Erection drawings show the placement of members in the final structure, and usually detail their weights. You design these mainly to aid fieldwork.
Falsework drawings show any supportive structures that you will need to temporarily cock around the primary structure.
Construction Plans for Dissimilar Building Parts
Allow's delve into each plan type in detail. For a await at the construction plans for a typical residential project, check out what the firm Donald A. Gardner Architects provides in i of its business firm plan sets.
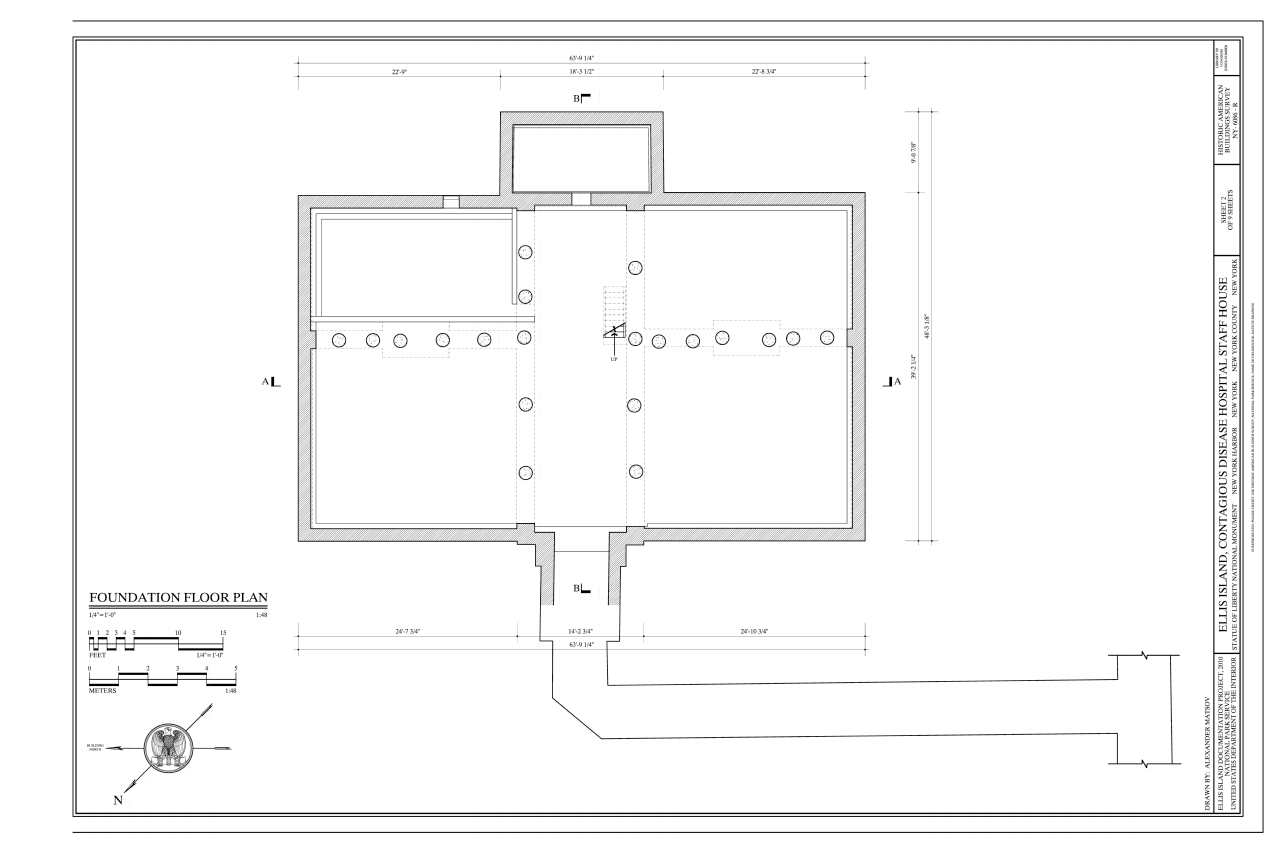
Foundation plans are a type of structural engineering programme. They can besides refer to subfloor plans or, in some cases, basement floor plans. They show the sizes, shapes, thicknesses, configurations, and elevations of foundation walls and footings, including interior load-begetting walls and exterior post footings. Foundation plans will too show the positioning of reinforcing confined and the connections and attachments via anchor bolts or weld plates between the foundation's structural members. These plans delineate excavated and unexcavated areas of the foundation.
A basis schedule accompanies the foundation program. It lists and describes all the footings upon which the structure will rest. Typically, there will exist extensive notes that explain how you reinforce structural members and define the concrete break strength requirements. The notes will besides depict how you test the force of the structure.
Framing plans are some other type of structural engineering plan. They detail the structural members that establish the building's framework: the size and positions of beams that appear in plans, and the joist and rafter space, layout, and size. Framing plans assistance builders lay out roof, floor, and ceiling structures.
A framing plan for a roof volition prove the various elements of the roof's structure, including dormers, hips, valleys, drains, and any equipment mounted on the roof. It also shows the roof pitch. Pre-engineered flooring and roof systems are also available. If yous use these, the manufacturer must provide engineering data to the builders, and building inspectors volition probably desire to review the plan before issuing a permit.
Floor plans are architectural plans that show the layout of each level of the structure. The drafter shows the layout from an overhead perspective that omits the roof and whatever upper floors. The floor plans illustrate the configuration of internal walls, doors, windows, and wall insets, such every bit fireplaces and chimneys. They also indicate the placement of permanent fixtures, such equally bathrooms, major appliances, and internal structures (stairways or elevators).
Each floor will have a flooring plan that includes a description of the intended uses of rooms or other internal spaces. The designer will indicate both door and window sizes and give dimensions, including lengths, widths, and internal square footages. Homeowners tend to be well-nigh interested in the floor plan, as it's perhaps the most straightforward and modifiable of all construction documents. The flooring plan as well makes it easy to motion-picture show how foot traffic will menstruum and how people will use the space.
1 uncommon variation of the flooring plan is the ceiling plan, which is a view of the ceiling as seen from below. Ceiling plans are only used for structures that have significant ceiling fixtures (so typically not residential projects).
Elevations are side views of a building that may prove either the exterior or the interior and omit external walls. Exterior elevations prove the placement of doors and windows, the external finish of the building, including whatsoever masonry or other decorative elements, and a side view of the roofing. They may too indicate the natural slope of the ground effectually the base of the edifice. Interior elevations show the superlative and placement of cabinets, countertops, and detailing, such as tiles on bathroom walls.
Elevations communicate peak, a dimension that bird's-eye views can't display effectively. Elevations also indicate the direction that an meridian faces, as the direction of sunshine and current of air patterns is of import when deciding how to place buildings, especially houses.
You should cross-reference elevations with flooring plans. Many people assume the architect will include an elevation for every exterior wall, but this is not always truthful. Compare the floor plans to the elevations to brand sure yous haven't missed annihilation.
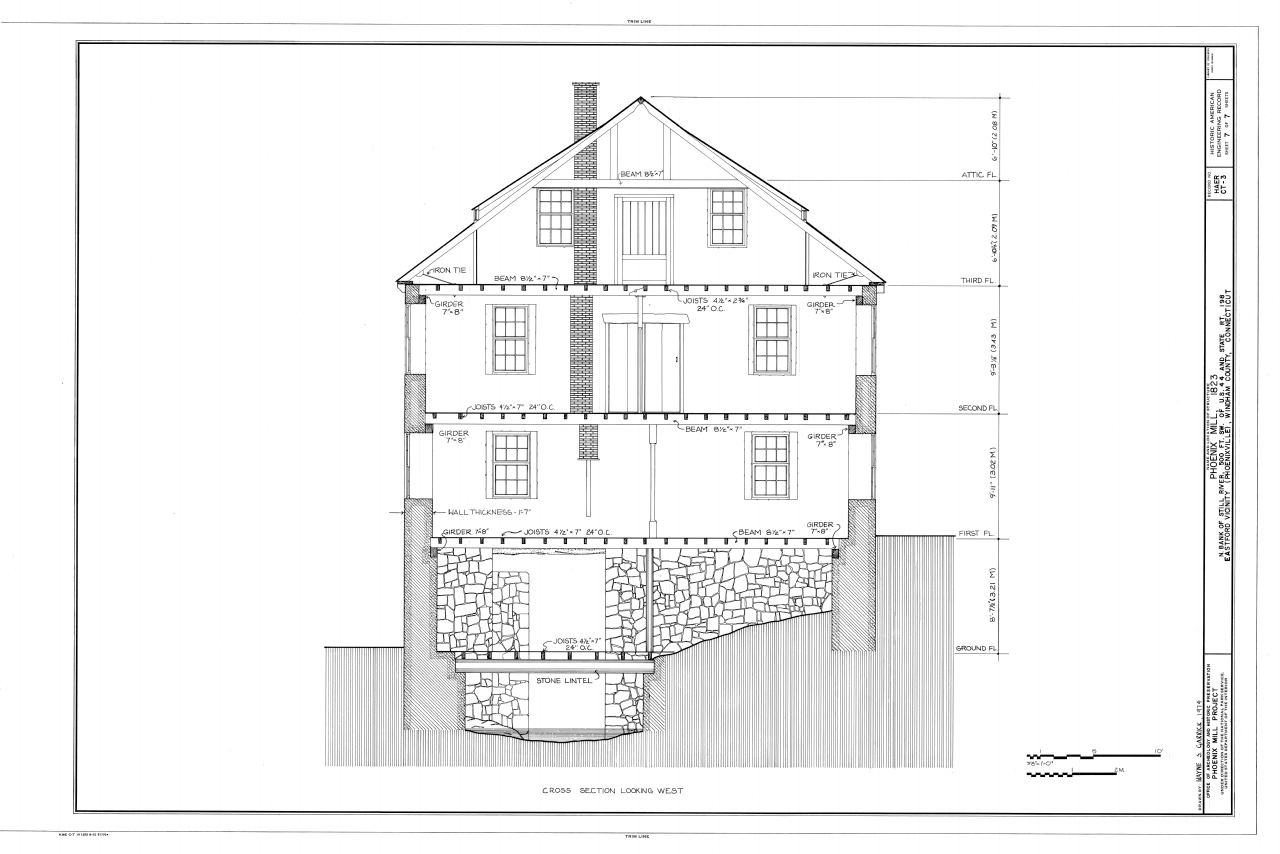
Cross sections are also a kind of side view, but these represent a vertical slice through the building to show all internal components. A cross section details both visible components, such equally stairs, sidings, and roofing, and concealed components, such as framing members, headers, and insulation. A cross section can pass through whatsoever level of the house, from the roof to the footings. Information technology captures things like cabinets and countertops, and besides internal framing components (this is important considering bird'due south-eye views can't draw them effectively). One common type of cross section is a wall cross section that shows both the inside and outside faces of walls as well equally internal components, such equally studs and insulation.
Where a simple residential project might merely require a few cross sections, a more than complicated commercial structure might need many more, since at that place are many variations in the components that go backside walls. You will cross-reference cross sections on plan views and elevations.
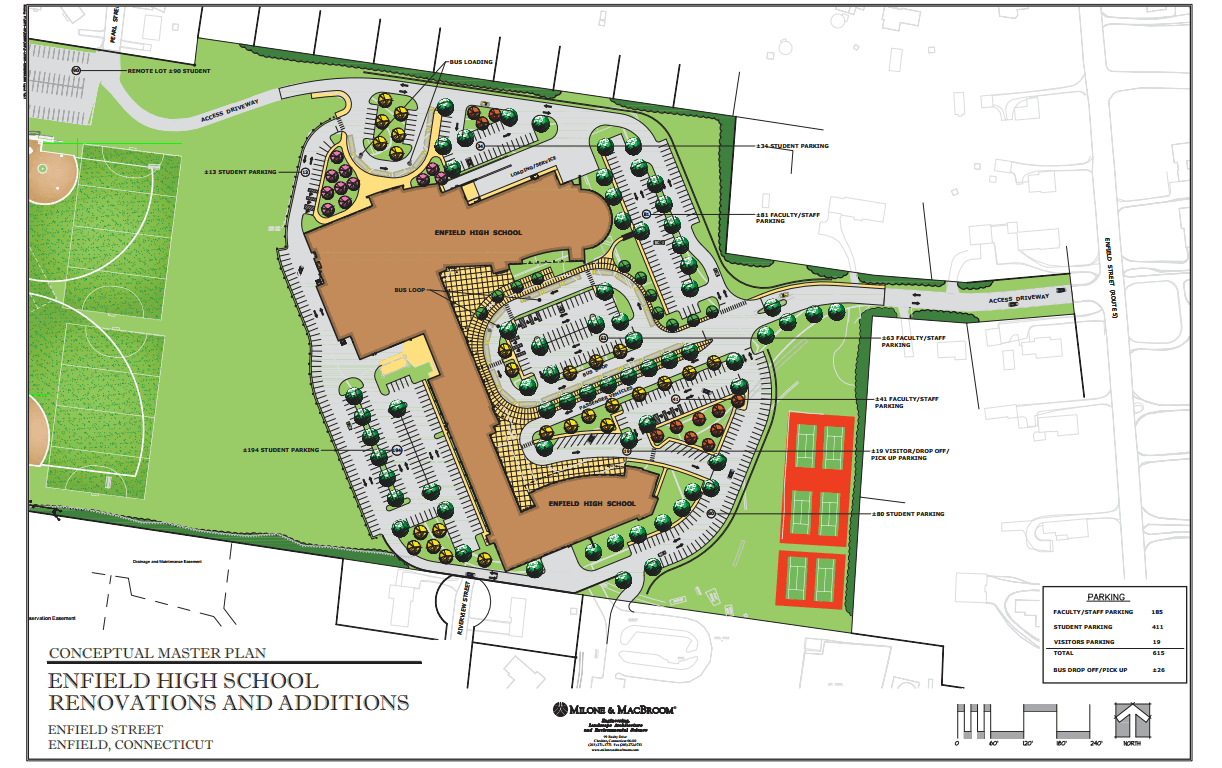
Site plans locate a edifice in the wider context of the land or packet. They detail the general dimensions and location of the site with reference to neighboring lots and their boundaries, and also mark the building's footprint on the site, and identify site landscaping features,roads, and pavements. Ultimately, the site programme summarizes work y'all will complete on site.
The site plan locates existing infrastructure that y'all need to protect during construction, such as sewer lines and utilities connections. Information technology contains information on the grade and summit of the construction site. These plans evidence the location of structures that are not part of the edifice proper, such as drainage systems and roads. Building inspectors considering whether to award a construction permit will check whether parking will accommodate the new structure'due south occupants.
Mechanical plans, like floor plans, are overhead views. They feature the mechanical components of a structure, such equally HVAC, gas lines, and plumbing. Putting these details on a split up sheet prevents conventional plans from becoming too crowded and difficult to read. Not all construction projects volition take separate mechanical plans - y'all usually only create them for projects with circuitous mechanical systems.
Mechanical plans will depict both the visible and concealed components of mechanical systems — both ventilators and ducts for a HVAC system, for instance. These plans may besides show whatsoever appliances connected to a mechanical arrangement, such every bit gas ovens. When examining mechanical plans with multiple all-encompassing systems, recollect that space restrictions may mean that subcontractors have to work in serial, not simultaneously.
Environmental plans address how the project will manage erosion and sedimentation of waters near the structure site. Given the amount of earth displaced and moved during construction, they're designed to ensure that all that soil doesn't end upward polluting and blocking nearby waterways. Ecology plans besides include procedures for minimizing plant removal and dealing with chemical spills.
The environmental plan typically lists a series of best management practices (BMPs) designed to minimize the harmful bear on on the environs. In many jurisdictions, an ecology programme is a requirement to go along with structure.
Schedules feature all the details an architect doesn't want to squeeze into a flooring plan. A schedule is a simple matrix of building component data, where each entry corresponds to a number that too appears on the flooring plan. Schedule information is highly detailed: A door schedule, for instance, will feature information on doors, door frames, and locks. A end schedule is a comprehensive table of finishes (pigment, flooring, etc.) in each room. Windows and light fixtures will also appear on schedules.
Schedules will also include items labeled OFCI (owner-furnished, contractor-installed), GFCI (authorities-furnished, contractor-installed), NIC (not in contract), and by others (those items provided outside the scope of a particular trade or contractor). In full general, the schedule will also prove delivery dates for items that you have ordered.
To learn more than about blueprints and how to read them, check out this course by Construction Experts Inc. The book Blueprint Reading: Structure Drawings for the Building Trades also covers the topic, and Francis D.Thousand. Ching'south Building Construction Illustrated is a helpful reference. Print Reading for Construction, past Walter Brown and Daniel Dorfmueller, is another resource.
How to Lay out a Building Footprint from Blueprints
Interested in learning exactly where a structure will lie on a lot? Y'all'll have to lay out the building'south "footprint," which is the area of land it occupies at ground level. Being able to practice this, or at least sympathize it very clearly, is a core piece of construction knowledge.
To starting time, look at the site plan to find reference points that will allow you to locate the structure. If the site plan doesn't make reference to existing landmarks or features of the landscape, chances are information technology uses a coordinate system comprising northings and eastings to locate the building. You'll also need to use an instrument called a total station theodolite (TST) to determine the building's coordinates. Remember, the smaller the lot and the closer it is to other structures, the greater the need for precision when locating the edifice'southward coordinates. Kickoff by locating the corners of one side of the building, and mensurate distances to landmarks to make sure yous've positioned the corners correctly. Work your fashion around until y'all've located all the corners.
Your next stride is filling in the lines between corners. There are a number of ways to practice this, depending on the blazon of construction that you intend to build: You lot might measure and locate column lines, foundation lines, or outside wall lines. An architect or builder can tell you which is most advisable, and yous'll need to acquire how the different line types announced on the site programme. Use a triangle-blazon rule to calibration distances on plans, as they're less probable to result in measuring errors. If y'all need to add distances, use a builder's computer, which will expedite mathematical operations based on dimensions. CAD plans as well help make up one's mind distances, specially within the exterior building line (OBL).
Building piece of work typically needs to start on level surfaces, then you'll too demand to plant the elevation, if any, from which work will commence. The elevation is computed with reference to nearby structures or to sea level (check out the Australian Height Datum). The site plan will indicate a measurement called the "meridian above the existing grade," or will use an existing vertical marker to show the acme.
Structure Safety Plans Can Salvage Lives
So far, we've talked almost construction plans specifically as documents that provide technical information about a construction and how to build it. These plans include blueprints, specifications, and schedules. But structure plans too refers to the results of the broader planning procedure that encompasses environmental, rubber, and quality plans.
Safety plans are of import because construction is hazardous, and the best mode to foreclose an accident is to conceptualize what could go wrong. In 2015, according to the Occupational Prophylactic and Health Administration (OSHA), ane in v private-industry worker fatalities — a total of 937 deaths — occurred in the construction manufacture. Near one in 10 U.S. structure workers will sustain injuries in any given year. Falls cause the most injuries.
Safety planning isn't as rigorous in small residential projects, but it is a regulatory requirement for large projects. OSHA standard 29 CFR 1926, "Safety and Health Regulations for Construction," defines structure project safety standards, and OSHA has 10 construction prophylactic plan requirements for the construction manufacture.
Safety planning revolves effectually run a risk reduction and hazard elimination to avoid on-site accidents. It'due south almost effective when integrated proactively with project planning and so that information technology evolves with site and ecology conditions.
Prophylactic planning is an integral part of construction design and scheduling. Builders who place potential hazards for construction crews — a do called job gamble analysis — can proactively mitigate them by implementing safety measures and emergency response equipment. This extends from observing occupancy limits for confined spaces to making fire safety equipment available close to where it might be needed. These risk-command steps, along with plans for what to do if an accident occurs, are the project'southward rubber management strategies.
If you need to compile or evaluate a construction programme, it helps to know the traditional elements. Review OSHA'south safety checklist for construction. A construction safe plan must include certain sections and respond key questions, such every bit who is in charge of safe on site, what arrangements be for medical treatment, what safety preparation you will conduct, and the lockout/tagout procedures.
Use the checklist below equally a starting betoken for your site safety plan. However, call back that your terminal safety plan needs to exist specific to the hazards present in your unique circumstances. Follow all applicable regulations, such as OSHA requirements.
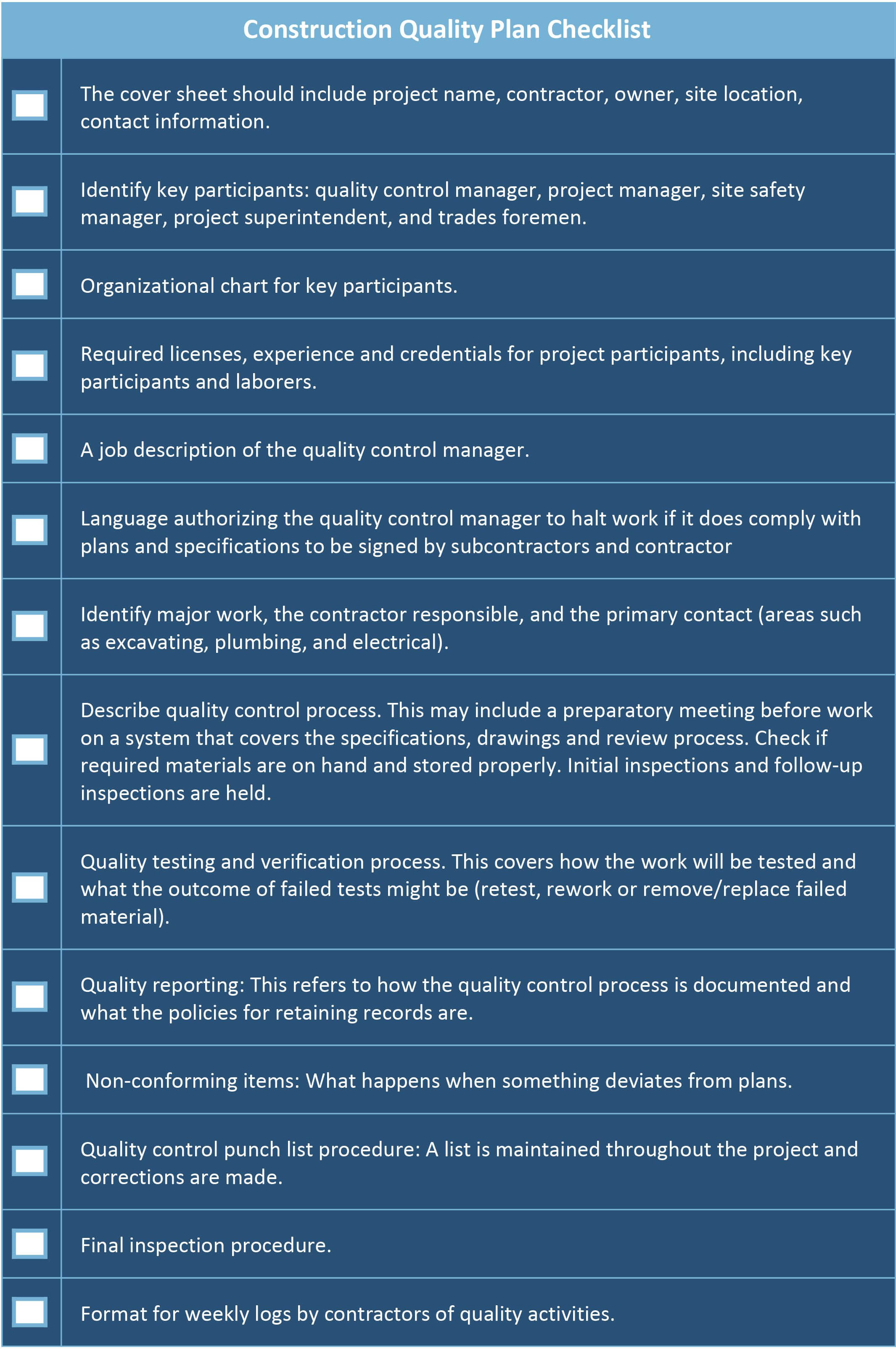
Download Construction Condom Plans Checklist
Quality Plans Help Builders Thrill Clients and Users
A structure quality plan is a document that explains how a contractor will come across the quality requirements for a specific project. It's not the aforementioned as a company's general quality policies, since it addresses quality direction for an individual projection.
Whether formally required in a contract or informally requested, the quality programme is an important function of the client-contractor working relationship. For the customer, it improves confidence in the contractor's ability to get the job washed and builds in a mechanism for accountability. For the contractor, information technology ensures all parties are on the aforementioned folio and that the projection upshot will enhance their reputation.
The quality plan for a project identifies those responsible for quality management and establishes protocols for quality-related communications. It highlights the regulations and industry standards that apply to a project, and explains procedures for assessing quality. Lastly, it explains how subcontractors comply with the plan and the quality requirements for materials procurement.
Ed Caldeira of First Time Quality explains what a good quality management plan will tell a client:
- "Who is in charge of quality management on the projection, and what are their qualifications?
- How and when will y'all communicate quality-related issues to the contractor's personnel and the customer?
- What sort of quality oversight organization volition y'all put in place?
- How will you lot ensure quality from subcontractors and suppliers?
- What constitutes satisfactory quality for a project? What quality standards will y'all set?
- How will y'all test quality?
- Should they arise, how will you set up quality issues?
- How will you lot assess the project's deliverables quality?"
When developing a quality control plan for construction, consider roofing the following topics:
Download Construction Quality Plans Checklist
Engineering Eases Structure Planning
Earlier nosotros talked near the difficulty of working with blueprints. Construction has lagged behind other major industries in digital adoption, and planning engineering solves many of the issues and constraints of conventional paper construction plans.
Construction planning technology covers a number of software solutions, from scheduling apps to SaaS suites. The design modules reduce the time and coin costs of manually updating structure plans and reworking pattern elements.
The most helpful features include the following abilities:
- View, edit, and share drawings
- Access plans and documents in the field from mobile devices
- Zoom in with high-resolution plans to capture detail
- Ensure sheet version control
- Store in the cloud
- Retrieve plans chop-chop with fast-loading optimization
- Annotate with markups and as-built notes
- Take photos and share and archive them
- Automate quantity takeoff
These capabilities unlock some stiff advantages for builders and project managers. With these tools, collaboration flows more easily, anybody always has the electric current set of plans, accuracy rises, and all participants (whether they are in the office or the field) share the same data. Scheduling engines give contractors a competitive reward by increasing productivity. Quality also rises since project teams tin can update and share blueprints, punch lists, specifications, and RFIs instantaneously.
These capabilities increment efficiency. One construction software visitor surveyed its customers, who said that on average they saved $fifteen,000 in labor per twelvemonth per employee past using a construction solution.
That fiscal do good accrues from greater efficiency. But not using newspaper plans also saves on printing costs. Aside from architect fees, plans typically price $2 to $4 a page to print. The documents sets for large commercial projects will have hundreds of pages, and many project managers, supervisors, and foremen need their own set. You'll besides have to reprint sheets when in that location are changes, and since changes are common, the costs speedily add up. Of course, using digital plans means squad members must have tablets or laptops and a subscription to an application that generally has a fee.
These tools would not exist without other technological innovations in the construction plan globe, such as CAD and building information modeling (BIM). CAD was the precursor to BIM: It began as the groundbreaking use of software to design physical components, specially in manufacturing, though ceremonious engineering projects used it as well. Designers then embraced it for cartoon plans.
BIM is the side by side phase in construction pattern. It goes beyond two-dimensional CAD to 3D building information models that offer comprehensive data for entire structure projects. BIM provides highly circuitous digital representations of building design, and it's stretching beyond 3D visualization to so-called 4D and 5D integration of time and cost information.
CAD made it easy to view, edit, and share construction drawings, with no perceptible loss of quality. CAD plans likewise make dimensions easier to measure. These drawings mimic some of the strengths of traditional paper plans only are easier to share and marking up.
Glossary of Central Terms in Construction Plans
Below, y'all'll find a useful list of terms concerning construction plans.
- Building Envelope: The consummate set up of physical structures that split up a edifice's interior from its outside, such as walls, roofs, and floors.
- Ceremonious Drawing: A blazon of site program designed for apply by civil engineers that shows topographical features, landscaping, and utility connections.
- Eastings: A gear up of eastward-extending coordinates on a geographic plane. Together with northings, they establish a organisation of Cartesian coordinates that you use to plot building locations with reference to already existing landmarks. Encounter also northings.
- Ground: A component of a building'due south foundation that transfers the weight you place on walls to the ground. Compared to other types of foundations, footings are typically quite shallow, though there are restrictions on minimum ground depth.
- GFCI (Government-Furnished, Contractor-Installed): This acronym, used on structure plans and specifications, indicates materials or components that the projection owner will procure — in this case, the project owner is the regime, and they provide the GFCI to the contractor for installation. The GFCI mark on construction plans tells cost estimators which piece of work items they do non need to procure. Information technology'south also a reminder for the contractor to coordinate a commitment schedule with the authorities.
- Level of Detail and Level of Evolution: Nosotros oftentimes refer to both of these terms as LOD. Level of detail describes the increasing corporeality of particular in graphical representation as construction plans become more refined. A conceptual drawing is much less detailed than a detailed drawing. Level of development describes how much evolution and engineering have gone into the feature.
- NIC (Non in Contract): This acronym, used on structure plans and specifications, indicates piece of work items that are not the main contractor's responsibility to deliver. The projection possessor either delivers these work items or contracts with another party to take them deliver the items. The NIC marker on construction plans tells price estimators which work items they should non bid for.
- Northings: A set of due north-extending coordinates on a geographic aeroplane. Together with eastings, they constitute a organization of Cartesian coordinates that yous utilize to plot building locations with reference to already existing landmarks. See too eastings.
- OFCI (Owner-Furnished, Contractor-Installed): This acronym, which you use on construction plans and specifications, indicates materials or components that the project owner volition procure and provide to the contractor for installation. The OFCI marker on construction plans tells cost estimators which work items they practise not need to procure. It'south also a reminder for the contractor to coordinate a commitment schedule with the owner.
- Outside Building Line: A commonly used reference bespeak in structure drawings that helps planners decide distances to other structural components.
- Quantity Takeoff: A technique for estimating the types and quantities of materials and labor required to complete a structure project. The quantity takeoff is part of the project cost estimating procedure. It gets its name from the mode toll estimators would originally perform the office, when they would "accept off" quantities of all materials from blueprints and specifications to gear up an itemized list.
Better Construction Plans with Smartsheet for Structure
From pre-construction to project closeout, keep all stakeholders in the loop with real-time collaboration and automated updates and then you tin can brand better, more informed decisions, all while landing your projects on fourth dimension and within budget.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and written report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more constructive and get more done. Report on key metrics and go existent-fourth dimension visibility into work as it happens with scroll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your squad connected and informed.
When teams accept clarity into the work getting washed, in that location's no telling how much more than they can accomplish in the aforementioned amount of time. Endeavor Smartsheet for gratis, today.
Source: https://www.smartsheet.com/how-to-read-construction-plans





0 Response to "How to Create Marketing Drawings Architecture Plans Representation"
Postar um comentário